Physiological effect of the electricity
Content:
Effect on the heart
The effect of the current in a body can take several forms.
- Thermic effect – Burns (can be done with 10 mA if the contact takes few minutes.
- Tetanizing Effects – When an AC current is going through the body, muscles are contracted.
To calculate the current passing through the body many parameter have to be taken in consideration. In order to simplify the calculation, the Ohm's law is used with a body Impedance of 1000 Ω in average. We know what factors can make a difference in the effect of current on the body. One of the various physiological effects of an electric shock with an alternating current (AC) is death. Death is a possibility in three ways - the breathing centre in the brain is paralyzed, ventricular fibrillation, and paralysis of the heart. |
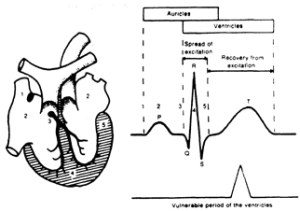
Definition
Definition : Vulnerable period
The vulnerable period covers a comparatively small part of the cardiac cycle during which the heart fibres are in an inhomogeneous state of excitability and ventricular fibrillation occurs if they are excited by an electric current of sufficient magnitude. Note. - The vulnerable period corresponds to the first part of the “T-wave” in the electrocardiogram which is approximately 10% to 20% of the cardiac cycle.