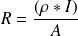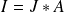2.1. Conductive part.
2.1.1. Electrical features
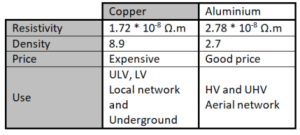
2.1.2. Mechanical feature
The conductor should be enough flexible to follow the complicated path of the conduits. There are:
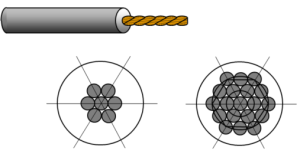
Multi strand conductors are made with several twisted strands. The strands are put in several layers.
The single strand conductor has one strand and the cross section can be up to 35 mm².

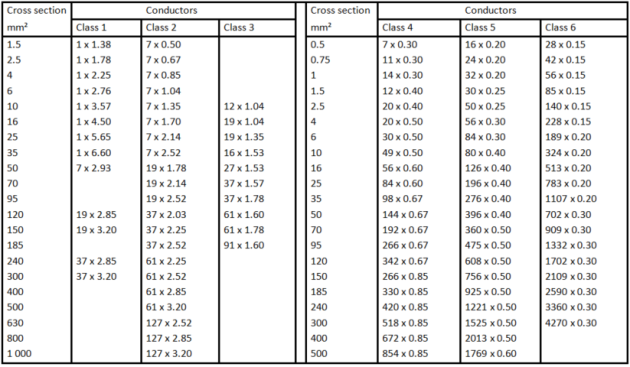
The flexibility of a cable depends of the number of strand for the same conductive cross section. The flexibility is defined in 6 classes. Class 1: less flexible, class 6 more flexible. We usually use classes 1, 2, 5, 6.
Standards
Cables for fixed installations: Classes 1 and 2
The flexibles: Classes 5 and 6
Copper welding cables: Class 6