Circuit breaker selection principles
Circuit breakers
Protective devices are used to:
guard against fires that might be caused by a faulty electric circuit (short-circuit, overload, insulation fault);
protect people against electric shock in the event of indirect contact.
The choice of protective devices must be optimized to provide absolute protection while ensuring continuity of service.
Although the protective devices are sometimes used as lighting circuit control units, it is recommended to install:
separate control devices (switch, contactor, impulse relay ...).
or an integrated control circuit breaker designed for lighting applications which withstands a larger number of switching operations
Circuit breakers are used to:
Protection of electrical distribution against short-circuits and overloads
Protection of loads against overloads
Advice : Choice of the breaking capacity
The breaking capacity of an MCB is its limit current that it can break in case of short-circuit. The breaking capacity value of an MCB must be higher than the highest possible short circuit current in the circuit it is protecting.
Advice : Choice of rating
The rating of a MCB is chosen according to the cable it will protect. for cable its depends of the cable cross section. The rating must be always less or equal to the rating of the device it will protect. e.g. a 16A or less MCB will protect 16A Sockets, 16A Switches.
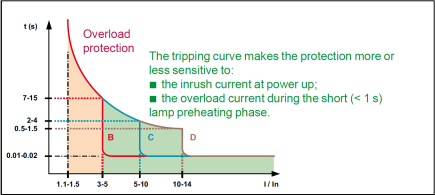
Advice : Choice of tripping curves
The choice of tripping curve depends on the load and the length of the cable.