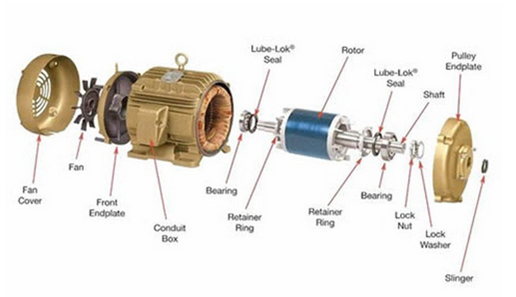
3. Constitution of an asynchronous machine
Note : 3.1. The stator circuit
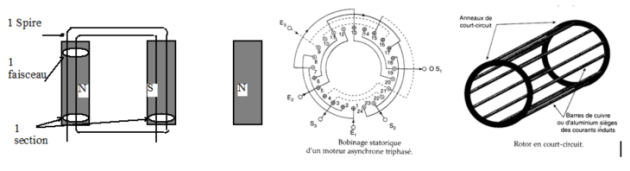
To produce a rotating magnetic field, a winding or stator winding is realized, with coils housed in stator slots.
Note : 3.2. Rotor circuit
The rotor is the seat of electromotive forces produced by the action of the magnetic field on the induced currents of the rotor circuit.
There are two types of rotor:
The rotor in short circuit or squirrel cage. The winding consists of copper or aluminium metal bars embedded in the magnetic circuit and short circuited by two rings.
The wound rotor: the winding consists of three star-coupled windings connected to the external circuit by three rings. This type of engine requires special equipment that allows obtaining a progressive start torque.
Note : 3.3. Winding concept
In three-phase, the stator is composed of three independent windings. Each of these windings is composed of sections housed in notches of the magnetic circuit.
The turn (spire): it includes a wire to go and a return wire, two active wires.
The beam (Faiceau): this is the set of conductors placed in a notch and travelled in the same direction by the current of a phase.
Section: It is formed by two beams connected by the coil heads. It is characterized by its number of turns and its pitch.
Section steep: This is the distance between two consecutive neutral lines. It is also called diametrical