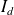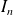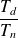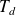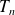4. Equations
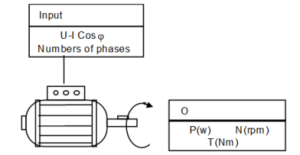
Definition : The electrical power absorbed by a three-phase asynchronous motor is
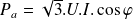
with:
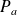 : Power in W (Watt);
: Power in W (Watt);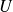 : Voltage in V (Volts);
: Voltage in V (Volts);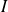 : Current in A (Amperes);
: Current in A (Amperes);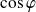 : cosine of the phase shift angle between current and voltage
: cosine of the phase shift angle between current and voltage
Note: The current and voltage measurements cannot give the power,
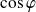 can vary between 0.1 and 0.2 empty until 0.9 at full load.
can vary between 0.1 and 0.2 empty until 0.9 at full load.
Definition : The mechanical power is that obtained on the motor shaft:
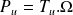
With
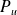 : Power in W (watt);
: Power in W (watt);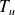 : Engine torque Newton-meter (Nm);
: Engine torque Newton-meter (Nm);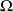 : angular velocity in radian per second (rad / s);
: angular velocity in radian per second (rad / s); : Rotational speed in revolutions per second (rps).
: Rotational speed in revolutions per second (rps).
Definition : Rated power:
This is the mechanical power available on the motor shaft at its rated speed.
Definition : Rated speed:
The nominal speed is the speed at nominal power. We distinguish the speed of synchronize (speed of the rotating field):
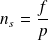
With
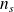 : synchronism speed;
: synchronism speed;
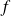 : frequency of the supply voltage;
: frequency of the supply voltage;
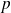 : number of pole pairs of the machine.
: number of pole pairs of the machine.
Definition : Rotation Speed:
The rotation speed of the motor is lower than the speed of synchronism. The difference is characterized by the slip
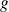 :
:
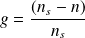
with
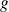 : Slip in %
: Slip in %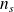 : Synchronious speed in rps
: Synchronious speed in rps : Real speed in rps
: Real speed in rps
Definition : Nominal current:
This is the value of the current absorbed by the machine at rated power and rated voltage
Definition : Power factor and efficiency:
The efficiency and the power factor change according to the load. They are given for the nominal power of the machine.
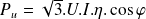
With:
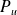 : rated useful power;
: rated useful power;
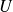 : voltage between nominal phase;
: voltage between nominal phase;
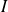 : rated current;
: rated current;
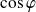 : power factor;
: power factor;
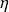 : efficiency.
: efficiency.
Definition : Current ratio:
This is the ratio between the current absorbed at start-up and the rated current. In case of direct start, it varies from 6 to 8. | 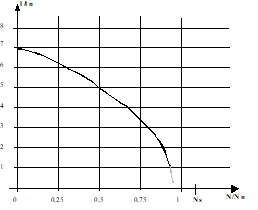 |
Definition : Torque ratio:
This is the ratio between the starting torque and the nominal torque. It is between 1.5 and 3 depending on the construction of the machine. | 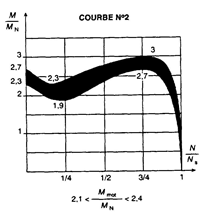 |