5. Speed variation of three-phase asynchronous machines
5.1. Action on the number of pairs of poles
This is the case of motors with separate windings or DAHLANDER type. There is an action on the number of pairs of poles.
Definition :
The formula
 shows that the speed can be varied by changing the number of poles.
shows that the speed can be varied by changing the number of poles.
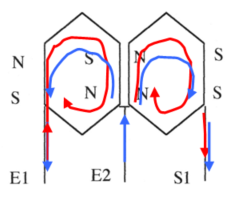 | Let the representation of the windings of a phase: • If we supply the simplified winding in E1, we obtain 4 poles; • If the simplified winding is supply to E2, 2 poles are obtained. This solution requires the inputs and midpoints of the phases to be accessible for coupling |
Coupling plate | 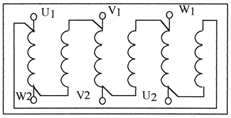 |
Method : Connection Low Speed
Connection Delta serie
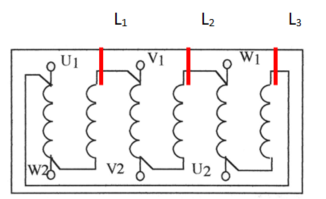
Method : Hight speed
Connection Star Parallel
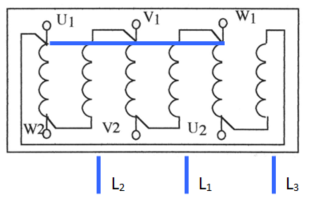
5.2. Action on the slip
Slip variation can only be used if the motor is a wound rotor. By inserting rotor resistors, it is possible to obtain several operating points. (Modification of R2). (At constant frequency and voltage)
The speed depends:
| 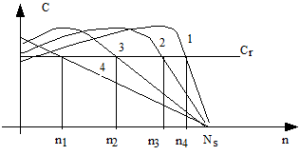 |
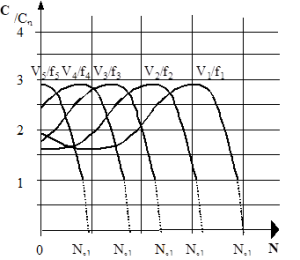
5.3. Frequency action
The speed is directly related to the frequency of the supply voltage. So a variation of f makes it possible to vary the speed. This method is commonly used for powers below 500 kW. It is important to keep the V / f ratio constant because it gives a constant torque. (See equations). So a variation of f is subject to a variation of V. In this case
|
This type of control is very common because it allows operation of the machine at any point of the torque-speed characteristic.
Method : 5.3.1. Principle of obtaining operation at constant V / f
The single-phase or three-phase voltage of the network is converted into a DC voltage via the rectifier bridge and the filter capacitors.
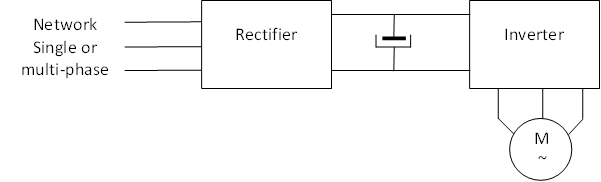
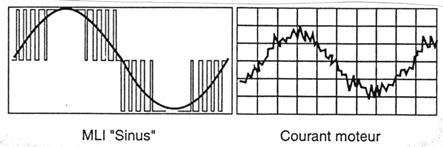
This DC voltage is cut by an inverter bridge to give a succession of pulses of variable width (PWM), modulation of pulse width.
The adjustment of the width of the pulses and their repetition make it possible to obtain a variable frequency while maintaining the constant V / F ratio;
The cutting, according to the PWM technique, ensures a smooth and steady rotation of the machines thanks to a form of output current close to the sinusoid;
The inductance of the motor realizes the smoothing of the current;
Note : 5.3.2. Output characteristics
Frequency converters provide higher frequencies than the network frequency;
Make sure that the engine supports speeding.
Variation of speed when starting an induction motor
The electronic starter is based on a gradual rise in the motor supply voltage during the start-up phase.
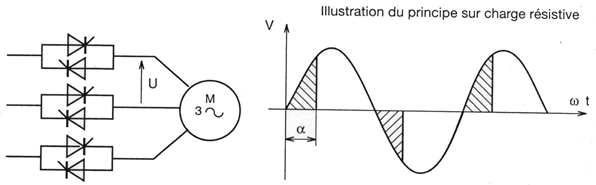
The voltage variation is obtained via a dimmer whose circuit consists of six thyristors mounted "head-to-tail" by two in each phase of the network.compose de six thyristors montés “tête bêche” par deux dans chaque phase du réseau.
As a function of the time and the starting time of the thyristors, the dimmer makes it possible to deliver a variable effective voltage across the motor and at a fixed frequency.
The control of the Dimmer is usually done by a voltage ramp
The advantages of this type of starter are:
Mechanics:
Elimination of sudden starts;
Reduced wear of mechanical transmissions;
Electric:
Reduction of the dimensioning of the network;
Possibility of cascading several engines;
Reduction of starting current.
The major disadvantage of this type of starter is the starting torque which is very low. This type of starter is mainly used for machines with zero starting torque. Exp. : Fan, Pumps ...
An example of electronic starter is the DIJISTART or Altistart.